FORTUNE -- In May, less than a month after the blowout of the Deepwater Horizon oil rig in the Gulf of Mexico, a key milestone was achieved with little notice: Total U.S. supplies of petroleum and products refined from it (including the Strategic Petroleum Reserve) surpassed 1.8 billion barrels, reaching the highest level in the last 20 years. Since then the total has continued to edge upward, hitting 1.87 billion barrels in the week ended August 27, according to the Energy Information Administration.
FORTUNE -- In May, less than a month after the blowout of the Deepwater Horizon oil rig in the Gulf of Mexico, a key milestone was achieved with little notice: Total U.S. supplies of petroleum and products refined from it (including the Strategic Petroleum Reserve) surpassed 1.8 billion barrels, reaching the highest level in the last 20 years. Since then the total has continued to edge upward, hitting 1.87 billion barrels in the week ended August 27, according to the Energy Information Administration.
Despite the Iraq War and the resulting production disruptions, despite the moratorium on drilling in the Gulf, despite turmoil in Nigeria and ongoing cross-border transshipment quarrels in Central Asia and the multiple, repeated declarations that "peak oil" has arrived and supplies will inevitably dwindle, the United States has more petroleum on hand today than it has had since at least the beginning of the first Gulf War.
Part of that surplus comes from increased oil and gas production, particularly from ongoing production in the non-OPEC countries (including the U.S., where a "shale gas boom" has created a natural-gas glut). It also comes from flat demand due to the stumbling economic recovery and changing consumer behaviors. Neither of those factors is guaranteed to last. But as the summer driving season passes and students head back to school, awareness has gradually dawned that we may be looking at an oil surplus for years to come.
"In the last 18 months we've seen this big trend emerge," says David Kirsch, research director at PFC Energy in Washington, D.C. "We spent five to 10 years in a supply-constrained market, characterized by the growth of the BRIC countries [Brazil, Russia, India and China] and concerns over the security of supplies."
Now, Kirsch remarks, because of the financial crisis and the time it will take to pare down the debt of the major OECD nations, demand growth over the next decade is likely to be lower than previously forecast.
A new forecasting model
Official estimates of future oil supplies don't yet reflect this emerging consensus. Believing that "world oil prices will rise slowly as world oil demand increases because of projected global economic growth, slower growth in non-OPEC oil supply, and continued production restraint by members of the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)," the EIA forecasts that the spot price for West Texas Intermediate crude will start climbing again, averaging $81 per barrel in the fourth quarter of this year and $84 per barrel in 2011.
If government experts are wrong, though, we could see persistent surpluses and an oil price drifting toward $50 a barrel or even lower -- far below the $75-per-barrel that King Abdullah of Saudi Arabia called a "fair price for oil" last year. Economists and policymakers have only begun to contemplate what that means.
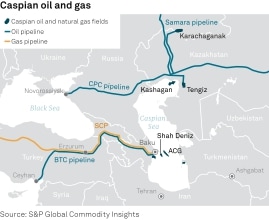
New oil supplies are coming primarily from Central Asia and Iraq, where nearly a dozen major contracts have been finalized with foreign producers in 2010. The largest prize is the Rumaila Field, in southeast Iraq near the head of the Persian Gulf, with proven reserves 18 billion barrels. BP and China National Petroleum have signed a contract to jointly develop Rumaila. A report from the U.S. Special Inspector General for Iraq Reconstruction, issued in July, said that Iraqi production, currently around 2.4 million barrels per day (bpd), could reach 12 million bpd by 2017. Saudi Arabia currently produces around 8 million barrels a day.
In Central Asia, the grandiose predictions for the Caspian Sea basin heard in the late 1990s - "another Saudi Arabia" - are finally approaching reality. Kazakhstan, home of the two largest oil finds in recent decades -- the super-giant Tengiz and Kashagan fields - is building more pipeline capacity heading east, to the vibrant markets of East Asia, rather than west, through the tangled pipeline politics of the Caucasus.
Even Israel, long one of the biggest oil importers in the Middle East, is getting into the act. Last year the U.S. Geological Survey reported that Israeli waters in the Eastern Mediterranean contain more than 120 trillion cubic feet of recoverable gas reserves -- and new discoveries have added another potential 24 trillion or so since that report came out.
Questioning peak oil
At the same time, consumers have finally responded to higher gas prices and, perhaps, concern over the environmental impacts of burning fossil fuels. Miles driven by U.S. motorists have fallen over the last couple of years for the first time since such statistics have been collected, indicating that the American love affair with the automobile could be waning. And gasoline demand in China, the world's largest automotive market, may not skyrocket after all, as the government ramps up its drive to replace internal combustion engines with electric vehicles.
An Israeli economy running on, and exporting, large domestic supplies of natural gas is only the most glaring of the geopolitical game-changers that $50-per-barrel oil would entail. Big growth in Iraq's oil industry would lead that country into discussions, and possible disputes, with Saudi Arabia over OPEC's production quotas. The worldwide gas surplus has already reduced the incentive and ability for Vladimir Putin's Russia to engage in power games with gas importers in Eastern Europe. And, of course, cheaper oil from non-OPEC nations could limit the political focus in the U.S. on foreign oil supplies -- and reduce Congress's urgency to pass a comprehensive clean-energy bill.
More than anything, though, the looming oil surplus calls into question the concept of peak oil, at least in the near future, along with the whole science of forecasting future oil supplies. Adam Brandt, a professor at Stanford's Department of Energy Resources Engineering, released a study last month examining the various models that have been used to predict the future of world oil supplies. "Data do not support assertions that any one model type is most useful for forecasting future oil production," Brandt concludes. "In fact, evidence suggests that existing models have fared poorly in predicting global oil production."
In other words, get ready for $50 oil.